Flat-Coated Retriever
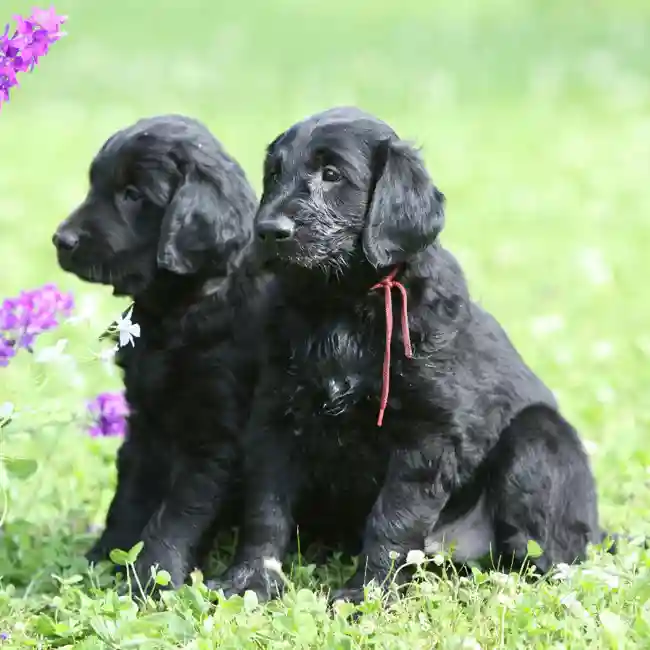

The Peter Pan of the Sporting Group, the forever-young Flat-Coated Retriever is a gundog of relatively recent origin. Happy, self-assured, and willing to please, a good Flat-Coat will retrieve a duck or a show ribbon with equal aplomb.

Ask About Flat-Coated Retriever ?
Breed Traits
General Appearance
The Flat-Coated Retriever is a versatile family companion hunting retriever with a happy and active demeanor, intelligent expression, and clean lines. The Flat-Coat has been traditionally described as showing "power without lumber and raciness without weediness." The distinctive and most important features of the Flat-Coat are the silhouette (both moving and standing), smooth effortless movement, head type, coat and character. In silhouette the Flat-Coat has a long, strong, clean, "one piece" head, which is unique to the breed. Free from exaggeration of stop or cheek, the head is set well into a moderately long neck which flows smoothly into well laid back shoulders. A level topline combined with a deep, long rib cage tapering to a moderate tuck-up create the impression of a blunted triangle. The brisket is well developed and the forechest forms a prominent prow. This utilitarian retriever is well balanced, strong, but elegant; never cobby, short legged or rangy. The coat is thick and flat lying, and the legs and tail are well feathered. A proud carriage, responsive attitude, waving tail and overall look of functional strength, quality, style and symmetry complete the picture of the typical FlatCoat. Judging the Flat-Coat moving freely on a loose lead and standing naturally is more important than judging him posed. Honorable scars should not count against the dog.
Size, Proportion, Substance
Head
Neck, Topline, Body
Forequarters
Hindquarters
Coat
Color
Gait
Temperament
Character
Group
Sporting
About
History
Standard
Nutrition
Grooming
Exercise
Training
Health
All pets have found there homes! Sign up to be notified when new pets are added so you don't miss out.